Tagging
Classify Text into Labels
Tagging means labeling a document with classes such as:
- sentiment
- language
- style (formal, informal etc.)
- covered topics
- political tendency
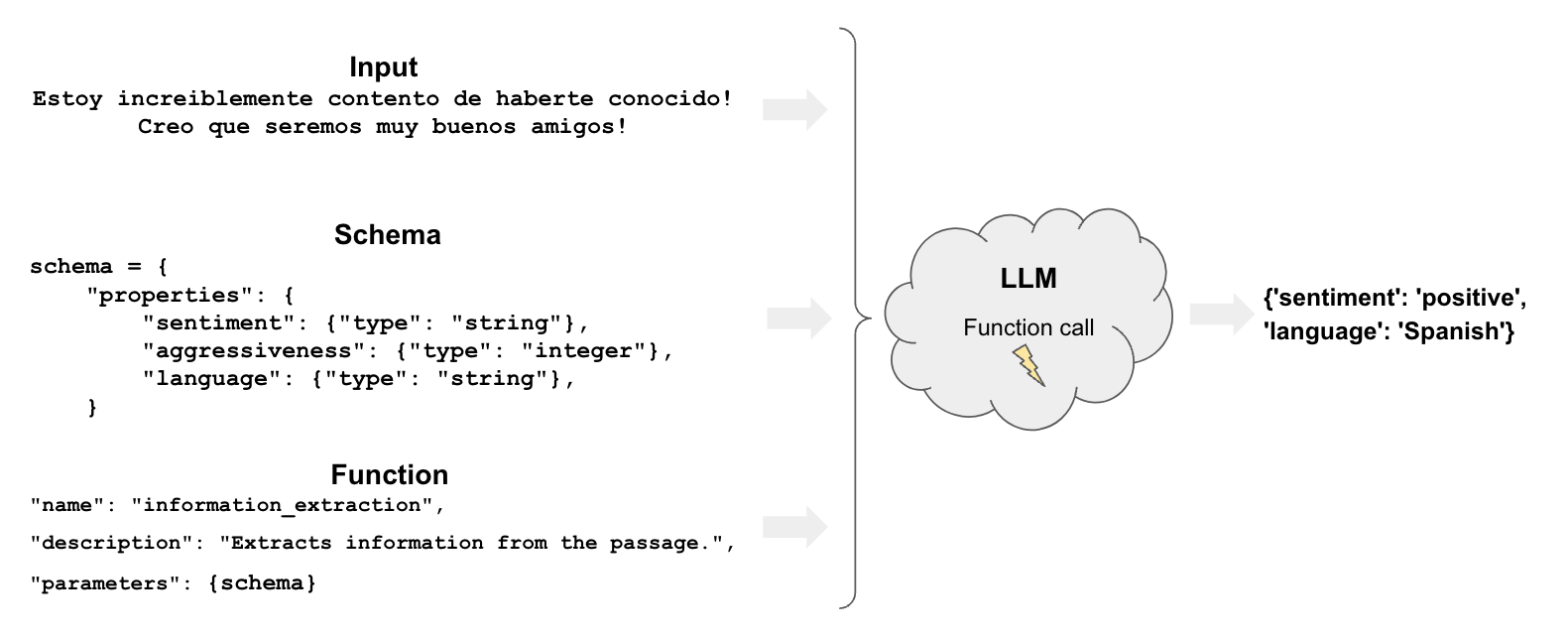
Overview
Tagging has a few components:
function: Like extraction, tagging uses functions to specify how the model should tag a documentschema: defines how we want to tag the document
Quickstart
Let's see a very straightforward example of how we can use OpenAI tool calling for tagging in LangChain. We'll use the with_structured_output method supported by OpenAI models:
%pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain langchain-openai
# Set env var OPENAI_API_KEY or load from a .env file:
# import dotenv
# dotenv.load_dotenv()
Let's specify a Pydantic model with a few properties and their expected type in our schema.
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
tagging_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Extract the desired information from the following passage.
Only extract the properties mentioned in the 'Classification' function.
Passage:
{input}
"""
)
class Classification(BaseModel):
sentiment: str = Field(description="The sentiment of the text")
aggressiveness: int = Field(
description="How aggressive the text is on a scale from 1 to 10"
)
language: str = Field(description="The language the text is written in")
# LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125").with_structured_output(
Classification
)
tagging_chain = tagging_prompt | llm
inp = "Estoy increiblemente contento de haberte conocido! Creo que seremos muy buenos amigos!"
tagging_chain.invoke({"input": inp})
Classification(sentiment='positive', aggressiveness=1, language='Spanish')
If we want JSON output, we can just call .dict()
inp = "Estoy muy enojado con vos! Te voy a dar tu merecido!"
res = tagging_chain.invoke({"input": inp})
res.dict()
{'sentiment': 'negative', 'aggressiveness': 8, 'language': 'Spanish'}
As we can see in the examples, it correctly interprets what we want.
The results vary so that we may get, for example, sentiments in different languages ('positive', 'enojado' etc.).
We will see how to control these results in the next section.
Finer control
Careful schema definition gives us more control over the model's output.
Specifically, we can define:
- possible values for each property
- description to make sure that the model understands the property
- required properties to be returned
Let's redeclare our Pydantic model to control for each of the previously mentioned aspects using enums:
class Classification(BaseModel):
sentiment: str = Field(..., enum=["happy", "neutral", "sad"])
aggressiveness: int = Field(
...,
description="describes how aggressive the statement is, the higher the number the more aggressive",
enum=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
)
language: str = Field(
..., enum=["spanish", "english", "french", "german", "italian"]
)
tagging_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Extract the desired information from the following passage.
Only extract the properties mentioned in the 'Classification' function.
Passage:
{input}
"""
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125").with_structured_output(
Classification
)
chain = tagging_prompt | llm
Now the answers will be restricted in a way we expect!
inp = "Estoy increiblemente contento de haberte conocido! Creo que seremos muy buenos amigos!"
chain.invoke({"input": inp})
Classification(sentiment='happy', aggressiveness=1, language='spanish')
inp = "Estoy muy enojado con vos! Te voy a dar tu merecido!"
chain.invoke({"input": inp})
Classification(sentiment='sad', aggressiveness=5, language='spanish')
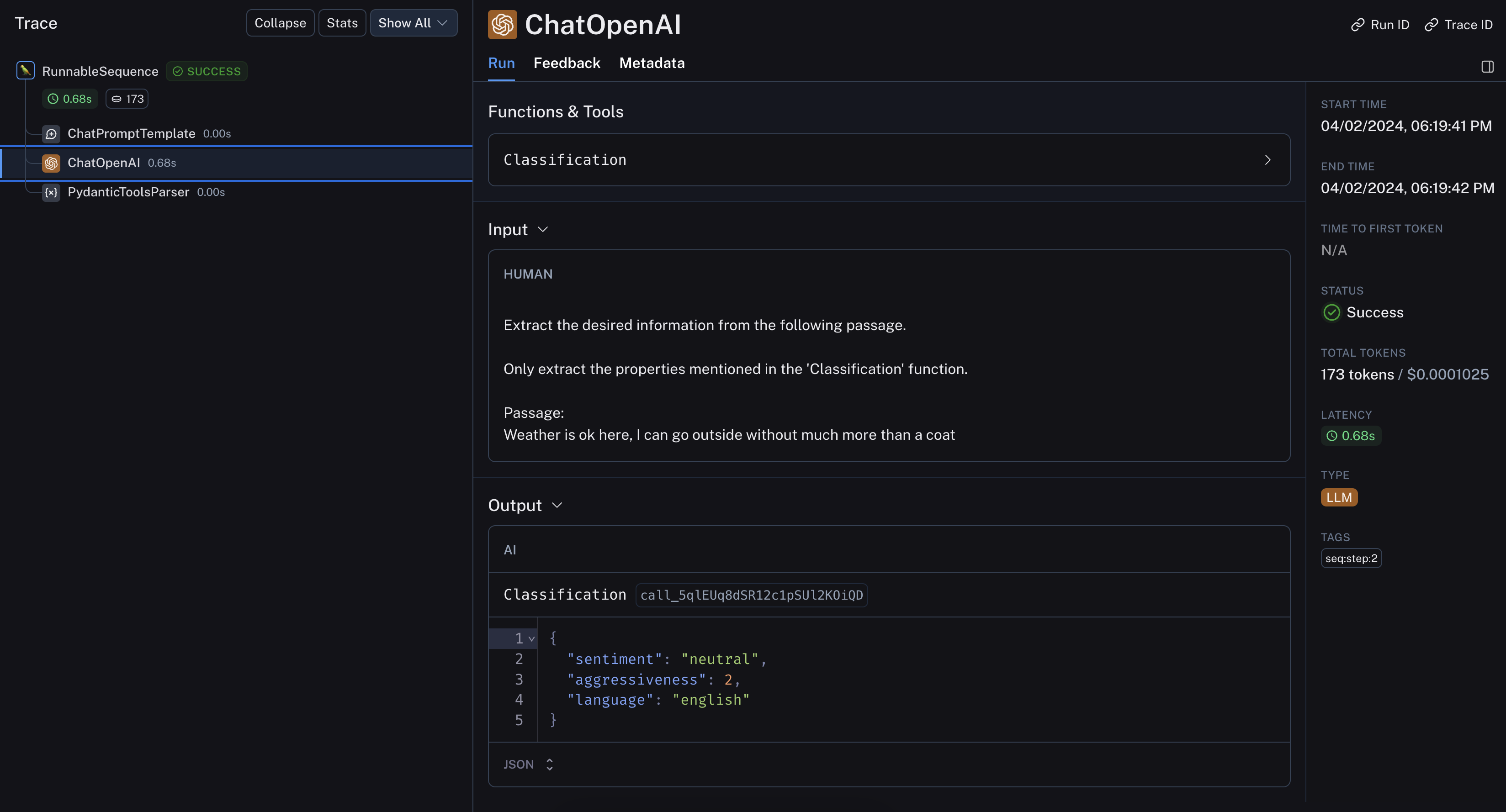
inp = "Weather is ok here, I can go outside without much more than a coat"
chain.invoke({"input": inp})
Classification(sentiment='neutral', aggressiveness=2, language='english')
The LangSmith trace lets us peek under the hood:
Going deeper
- You can use the metadata tagger document transformer to extract metadata from a LangChain
Document. - This covers the same basic functionality as the tagging chain, only applied to a LangChain
Document.